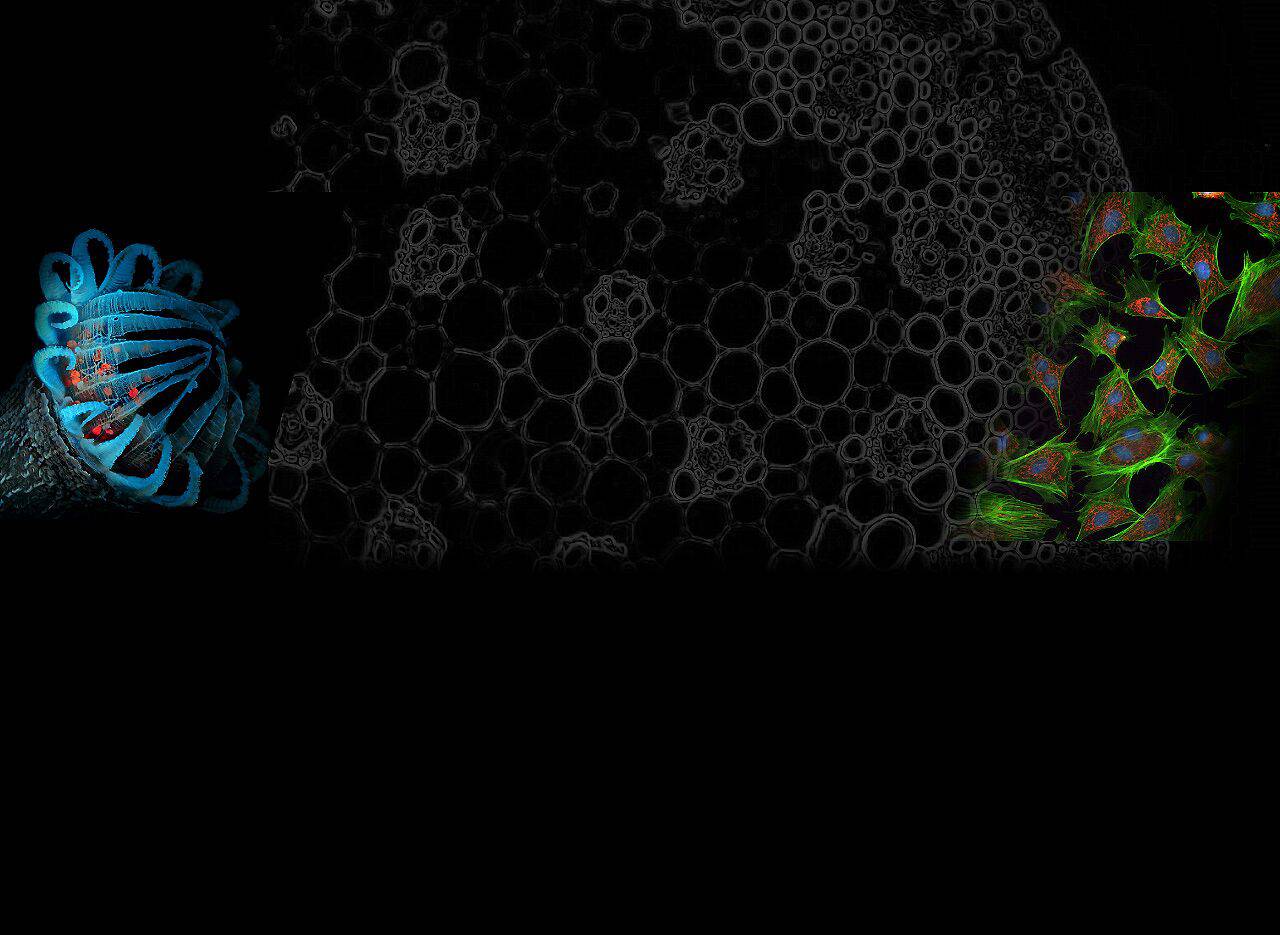
In fluorescence microscopy, Texas Red filters improve image quality and clarity. These filters are highly valued for their ability to reduce autofluorescence, resulting in clearer, more specific images. Laboratories around the world rely on Texas Red filters for their compatibility and reliability in scientific research.
An exceptional choice for microscopy is the Optolong Optics 30026 Single Band Texas Red Filters, which offer high brightness and high contrast imaging capabilities. This group of filters has precise wavelength specifications to ensure optimal performance when using Texas Red fluorophores.
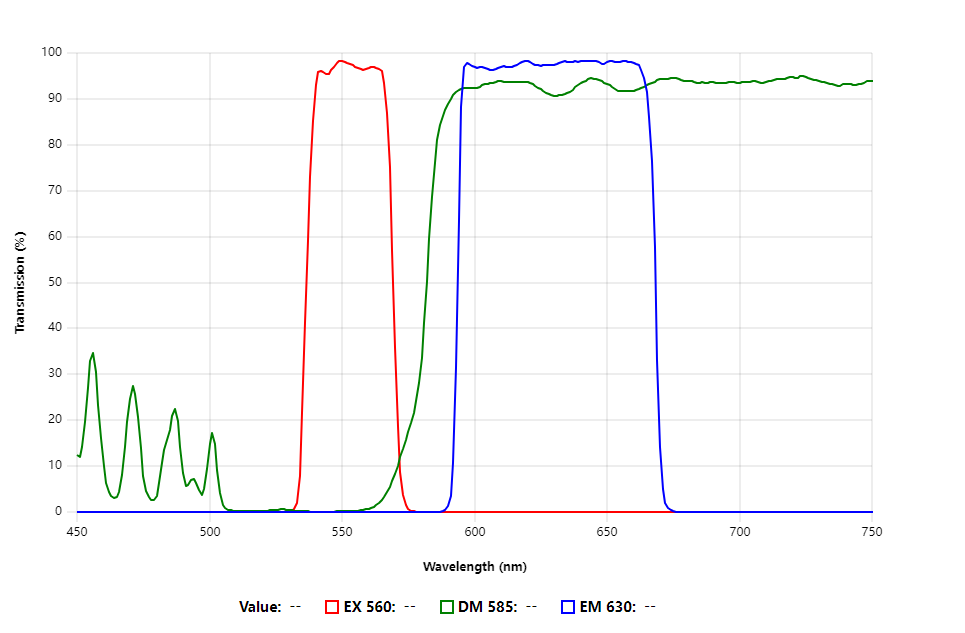
What is a Texas Red Filter?
Texas Red Filters effectively screen out specific fluorescent signals, allowing researchers to observe and analyze cells and tissues labeled with Texas Red Filters or similar fluorescent dyes. These filters improve image quality by isolating the desired wavelength of light for detailed microscopic analysis.
- Texas red filters play a fundamental role in fluorescence microscopy, ensuring accurate imaging by selectively allowing specific wavelengths of light to pass through while blocking unwanted signals.
- Common applications for Texas Red Filters include cellular imaging, tissue analysis, and molecular studies where the use of red fluorescence enables accurate visualization.
Why use Texas Red Filters?
The Texas Red Filter offers a variety of advantages and its unique properties improve the quality and specificity of fluorescence microscopy images, providing researchers with valuable insights about their samples. Some of its advantages over other filters are:
- High specificity: Texas Red filters precisely isolate red fluorescent signals, reducing background noise and improving image clarity.
- Enhanced Sensitivity: By effectively capturing light emitted by fluorophores such as Texas Red, these filters increase the sensitivity of microscopic samples.
- Cellular imaging: Texas Red filters are commonly used to study cellular structure and function due to their ability to highlight specific components within the cell.
Now that we have a brief introduction to what the Texas Red filter is, let’s go back and discuss 7 tips for using the Texas Red filter in fluorescence microscopy!
Tip 1: Proper Installation of Texas Red Filters: A Step-by-Step Guide
Preparing the Microscope
When preparing the microscope, first place it on a stable surface to avoid vibrations that may affect the installation process. Ensure the microscope is turned off before installing any filters to prevent electrical accidents.
Use a soft, lint-free cloth to clean the stage and surrounding areas, removing any dust or debris that might interfere with filter performance.
Inserting the Filter
When inserting the Texas Red filter, carefully remove it from its packaging, holding it by the edges to prevent fingerprints or smudges from getting on the glass.
Verify that it is properly oriented according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure optimal performance. Finally, gently slide the filter into its designated slot on the microscope, ensuring it fits securely without wiggling or becoming misaligned.
Common installation mistakes to avoid
- Rushing through the installation process without carefully following the manufacturer’s instructions may result in incorrect alignment and degraded image quality.
- Inserting a Texas Red filter with too much force may damage the filter and the microscope, thus compromising its functionality.
- Neglecting to clean the microscope on a regular basis can cause dust particles to accumulate on the filters, affecting their efficiency in isolating specific wavelengths.
Tip 2: Calibration and Alignment
To ensure accurate imaging results, calibration is a critical step in the microscopy process. By accurately adjusting your microscope’s settings, you can improve the quality of your observations and analyses.
How to calibrate the microscope
Begin by focusing on the objective lens for a clear view of the sample. Adjust the illumination intensity to optimize image brightness without causing overexposure. Fine-tune the contrast setting to distinguish different structures within the sample. The following are the tools needed for calibration:
- Slide with micrometer: accurately measure the field of view using a slide with a micrometer.
- Calibration slides: Use calibration slides of known size for size and distance measurements.
- Table Micrometer: Use a table micrometer for accurate calibration of magnification.
Proper calibration of the Texas Red filter will maximize its efficiency in isolating specific wavelengths during fluorescence microscopy examinations. Follow the steps below to properly calibrate the filter:
- Place the filter securely in its designated slot within the microscope unit.
- Ensure that there are no obstructions or misalignments that would interfere with the transmission of light through the filter.
- Verify that the excitation and emission wavelengths match those specified by the manufacturer for optimal performance.
By calibrating the microscope and accurately adjusting the Texas Red filter, you can achieve superior imaging with enhanced clarity and specificity.
Tip 3: Optimize Lighting Settings
Recommended Light Sources
For optimal illumination in a fluorescence microscope, it is recommended to use a high-quality LED light source that matches the excitation wavelength of the Texas Red filter to enhance image clarity.
LED lights with adjustable intensity settings offer the flexibility to control brightness levels, accommodating different samples effectively.
Balancing Brightness and Contrast
To optimize microscope images, adjust the light intensity to strike a balance between brightness and contrast. Fine-tune these settings to accentuate specific structures while preserving the overall clarity of the image.
Properly balancing brightness and contrast is essential for capturing detailed information without compromising the quality of the image.
Avoiding photobleaching
Photobleaching is a prevalent issue in fluorescence microscopy where fluorophores fade due to prolonged exposure to bright light.
To prevent this, optimize your illumination settings to minimize bright light exposure and regularly adjust the light intensity, ensuring the sample is not subjected to excessive light, which can cause damage and reduce the quality of your observations.
Tip 4: Sample Preparation Techniques
Fixation and permeabilization
First fix the sample using a suitable fixative to maintain its structure and integrity. Ensure that the cells are thoroughly permeabilized to allow effective penetration of the Texas Red dye. Use a permeabilization buffer containing a mild detergent to maintain cell morphology during the staining process.
Staining Solution
Prepare a fresh staining solution with the recommended concentration of Texas Red dye, and incubate the samples for the specified duration to achieve optimal labeling. After incubation, carefully wash off any excess dye to minimize background fluorescence and ensure clear imaging results.
Ensure consistent staining results
To ensure consistent staining results in microscopy, maintain uniformity in the staining solution to reduce variability between samples.
Carefully monitor the staining times to avoid under- or over-staining, which can impact the quality of images. Periodically check your staining protocols against both positive and negative controls to ensure the reliability of your results.
Tip 5: Image Acquisition and Analysis
Camera Settings
- Adjust camera settings to optimize image resolution and sharpness.
- Set the exposure time to effectively capture fluorescent signals.
- Fine-tune the focus to ensure clear and detailed images.
- Select the appropriate magnification for your sample.
Software Recommendations
- Utilize advanced imaging software for data acquisition and analysis.
- Choose software that offers image processing and enhancement capabilities.
- Use tools that quantify fluorescence intensity and analyze spatial distribution.
- Explore options for 3D reconstruction and multi-channel image stacking.
Analyze Fluorescence Data
- Evaluate fluorescence data to extract valuable insights from images.
- Measure fluorescence intensity to quantify signal strength in different regions of interest.
- Compare data from multiple samples or time points for comprehensive analysis.
- Evaluate the significance of experimental results using statistical analysis tools.
Click to learn: Do UV filters affect image quality?
Tip 6: Care and Maintenance of Texas Red Filters
- Wipe the surface of the Texas Red Filter with a soft, lint-free cloth.
- Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that may damage the filter coating.
- Clean in one direction to prevent smudging and to ensure that all debris is thoroughly removed.
- Store Texas Red filters in a clean, dry environment out of direct sunlight.
- When not in use, keep filters in a protective case to prevent scratches or dust buildup.
- Make sure each filter is properly labeled so that they can be easily identified during microscopic examination.
Solving Common Problems
If you are experiencing problems with Texas Red filters, here are some common problems and solutions:
- Faded images: Check the filter surface for dirt or residue and follow the recommended procedures for cleaning.
- Uneven illumination: verify that the filters are properly aligned within the microscope setup for even light transmission.
- Reduced contrast: Adjust illumination settings and verify proper alignment to enhance image contrast.
By maintaining regular cleaning habits and following proper storage guidelines, you can extend the life of your Texas Red filters and ensure consistent performance in fluorescence microscopy applications.
Tip 7: Application of Texas Red Filters

Combining Texas Red filters with other dyes opens up new possibilities for advanced imaging techniques in fluorescence microscopy. By multiplexing different fluorophores, researchers can observe multiple targets in a sample at the same time, providing a deeper understanding of cellular structures and interactions.
The use of Texas Red filters in cutting-edge research goes beyond traditional microscopy techniques, paving the way for innovative discoveries and advances in the life sciences.
Mixing Texas Red with other dyes
Combining Texas Red filters with complementary dyes such as GFP or DAPI provides a versatile approach to studying complex biological systems. This combination allows researchers to observe multiple cellular components simultaneously, providing a holistic view of cellular dynamics and function.
- Synergistic Imaging: Synergistic interactions between Texas Red and other dyes enhance imaging contrast and specificity, facilitating detailed analysis at the subcellular level.
- Dynamic tracking: By tracking multiple fluorophores in real-time, researchers can precisely and accurately reveal dynamic cellular processes and interactions.
Crosstalk Avoidance
Crosstalk between fluorophores can introduce artifacts and distortions in microscope images that can affect data accuracy. When using Texas Red filters with other dyes, crosstalk must be minimized through proper filter selection and optimization techniques.
- Spectral Separation: Careful selection of excitation wavelengths and emission filters helps prevent spectral overlap between different fluorophores, ensuring clear signal detection.
- Image Deconvolution: Advanced image processing algorithms can further eliminate crosstalk effects by deconvolving signals from overlapping channels, improving image clarity and accuracy.
Combining advanced multiplexing strategies with Texas Red filters opens up new ways to explore complex biological phenomena with unprecedented detail and clarity.
Summarizing
In this way, you can consider using Optolong Optics 30026 filters to meet your microscope needs and enhance your imaging experience.
The Optolong website also provides customized filter services. Come and contact us to get an accurate quote! Remember that high-quality filters are very important for accurate observation of fluorescence microscopy.
