A burning question many ask is, “Can mirrors reflect UV (ultraviolet) rays?” UV rays, the sun’s invisible beams, have an influence on both the environment and our health. Understanding how they interact with objects, like mirrors, is intriguing. Let’s start the fascinating world of mirrors and UV rays, uncovering the truths and myths surrounding this topic. It’s time to shed some light on this reflective mystery!
What Are UV rays?
UV rays, or ultraviolet rays, are a type of energy that comes directly from the sun. While we can’t see them with our naked eyes, they play a big role in our daily lives. The primary categories are UVA, UVB, and UVC. Out of these, UVA rays can lead to skin aging and potential long-term skin damage. UVB rays are the ones responsible for giving us sunburns. Thankfully, the Earth’s atmosphere protects us from UVC rays, which are the most harmful. To keep our skin safe, it’s essential to wear sunscreen, especially during sunny days, as it blocks these harmful rays effectively.

How Does UV Light Affect Humans?
UV light, or ultraviolet light, is a type of energy radiating from the sun. Although it’s invisible to our eyes, it has significant effects on our health and well-being. Understanding these effects can help us make informed decisions about our daily sun exposure.
UV rays come in three varieties: UVA, UVB, and UVC. Each one has a distinct impact on us:
1. UVA Rays
The general wavelength range is 320-420nm,these are the most common types of UV rays that reach the Earth’s surface. UVA rays penetrate deeply into our skin and are primarily responsible for premature aging. If you’ve ever noticed wrinkles, age spots, or a loss of skin elasticity, you’ve seen the impact of UVA rays. Prolonged exposure without protection can make our skin look older than its actual age. But that’s not all. UVA rays can also contribute to some skin cancers, emphasizing the need for protection.
2. UVB Rays
The general wavelength range is 275-320nm,these rays are somewhat less common than UVA but are much more harmful. They target the top layers of our skin, leading to sunburns. Repeated sunburns, especially during childhood, can dramatically increase the risk of skin cancer later in life. Moreover, UVB rays play a key role in the production of vitamin D within our bodies. A bit of UVB exposure is beneficial, but too much can be harmful.
3. UVC Rays
The general wavelength range is 200-275nm,fortunately, the Earth’s atmosphere does a great job of absorbing UVC rays. This means we don’t need to worry about them when we talk about sun exposure. However, it’s essential to know that UVC rays are used in man-made sources like germicidal lamps, which kill germs but can be harmful to humans.
Now that we know the different types of UV rays, let’s delve into how they affect us:
Skin Effects
Aside from the visible aging and sunburns caused by UVA and UVB rays, repeated UV exposure increases the risk of skin cancers like melanoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and basal cell carcinoma. It’s crucial to check our skin regularly for any unusual spots or changes and to see a dermatologist if something seems off.
Eye Effects
Our eyes are sensitive, and UV light can cause damage here too. Cataracts, a clouding of the eye lens, are linked to UV exposure. Other conditions like macular degeneration can also be exacerbated by UV light. Wearing sunglasses that block out 100% of UV rays can offer crucial protection.
Positive Effects
It’s not all bad news. As mentioned earlier, UVB rays help our skin produce vitamin D. This essential vitamin plays a role in bone health, immune function, and mood regulation. Many people, especially those in northern climates, can be deficient in vitamin D during the winter months. Brief sun exposure can help boost levels, but it’s a delicate balance between getting enough and overdoing it.
Spectroscopy knowledge
Optical coating curves less than 340nm cannot achieve high transmittance for now, generally 30-50% transmittance.
Safety Tips
So, how can we stay safe under the sun? Here are a few tips:
- Always wear sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection.
- Wear sunglasses that block out UV rays.
- Use hats and protective clothing during peak sun hours.
- Seek shade when the sun is at its strongest, typically from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- Stay informed and regularly check the UV index in your area.
Can mirrors reflect uv rays in spectroscopy?
Yes, mirrors can reflect UV (ultraviolet) rays In spectroscopy! Mirrors are designed to reflect light, and UV rays are a type of light. Just like they bounce back visible light, mirrors bounce back UV rays too. The shiny, reflective surface, often made of metals like silver or aluminum, does the job. However, not all mirrors reflect UV rays equally. The reflection quality depends on the mirror’s material and coating. So, while mirrors do reflect UV rays, some do it better than others. Always protect yourself from direct UV exposure, whether from the sun or reflected sources.
What do we suggest reflecting uv rays mirror for fluorescence imaging?
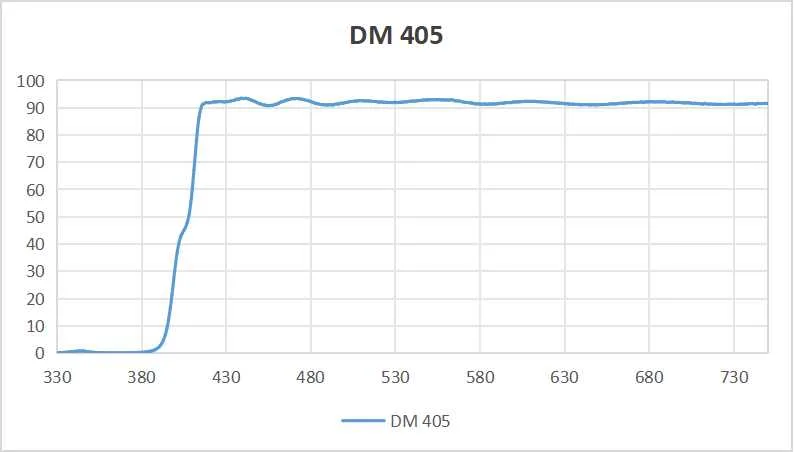
Selecting the best UV reflective mirror is crucial for optimal performance in fluorescence imaging studies. Our top recommendation is the “dichroic mirror 405nm.” Here’s why we suggest it:
Broad Spectrum: This mirror has a UV wavelegth band reflection range from 340-400nm, ensuring UV reflection.
High Reflectivity: The mirror has superior reflectivity and maximizes the reflection of the ultraviolet band.
Durable Construction: Made from premium materials, this mirror promises a long lifespan and robustness against wear and tear.
Versatile Usage:Whether for scientific, commercial or personal use, DAPI is suitable for fluorescence imaging research.
Consistent Performance: Users can expect consistent reflection rates, making outcomes predictable and reliable.
Brand Credibility: When investing in OPTOLONG’s dichroic mirrors, especially those in the ultraviolet band, choosing a trusted brand ensures quality.
Perfect spectral curves are a top contender for anyone looking for optical filters that reflect the ultraviolet band. It combines efficiency, safety, and durability, providing an unrivaled reflective experience. Make a wise choice and trust in its capabilities!
FAQs
Do all mirrors reflect UV rays?
Yes, a part mirrors can reflect UV rays, but the efficiency varies. The reflection quality depends on the mirror’s material and coating.
How do mirrors manage to reflect invisible UV rays?
Mirrors reflect light, both visible and invisible. The reflective surface, often a metal like silver, bounces back the UV rays, similar to visible light. Now,dielectric coated optical filters can also reflect the ultraviolet band.
Are there special mirrors that block UV rays
Yes, some mirrors have coatings or treatments that reduce or block UV reflection, some absorptive optical glass substrate can do the same thing.They are often used in specific industrial or scientific settings.
