IR cut filters block infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through. These filters improve image quality by preventing color shift and noise. The IR cut filter market is growing rapidly and is expected to expand significantly from 2023 to 2031.
IR cut filters are commonly used in digital cameras, security cameras, and various imaging applications. They ensure accurate color reproduction and improve overall image clarity. This article will explore the definition of IR cut filters and their role in applications.
What is infrared?
Infrared light exists outside the visible spectrum and cannot be seen by the human eye. Infrared light has a longer wavelength than visible light, ranging from 700 nm to 1 mm, and is generally classified into three categories:
- Near-infrared (NIR): shortest wavelength, highest frequency.
- Mid-infrared (MIR): intermediate wavelength and frequency.
- Far infrared (FIR): longest wavelength, lowest frequency.
Each category has unique properties, and the right infrared light can be selected based on the specific needs of the application.
What is an IR-cut filter?
An IR-cut filter blocks infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through. It improves image quality by blocking infrared light from reaching the camera sensor. All IR-cut filters ensure accurate color reproduction by blocking infrared light, which causes color shifts and distortions in images.
The filter works by reflecting or absorbing infrared wavelengths, a process that allows only visible light to reach the sensor, thereby improving image clarity.
Materials Used in IR Cut Filters
IR cut filters are commonly made using fused quartz, B270, float glass, and absorber glass. Each material has unique properties that affect the filter’s performance; fused quartz has high durability and excellent optical clarity; B270 has good transmission and cost-effectiveness. Float glass is widely used due to its availability and versatility; absorber glass can effectively block specific wavelengths.
Types of IR Cut Filters
There are several types of IR cut filters, each with a specific purpose. Here are some commonly used filters:
- Absorptive filters use materials that absorb infrared light while allowing visible light to pass through.
- Reflective filters reflect infrared light away from the sensor.
- Hybrid filters combine absorptive and reflective technologies for improved performance.
IR Cut Filter Manufacturing Process
First, the manufacturer selects the appropriate material, such as fused quartz or B270 glass. The selected material is cut and formed to meet specific size requirements. Next, a coating process applies multiple layers to achieve the desired filtering characteristics.
This coating can be either hard or soft, depending on the desired durability. Finally, the filters are rigorously tested to ensure they meet performance standards. Quality control measures ensure that each filter provides optimal results in its intended application.
Wavelength Range of IR Cut Filters
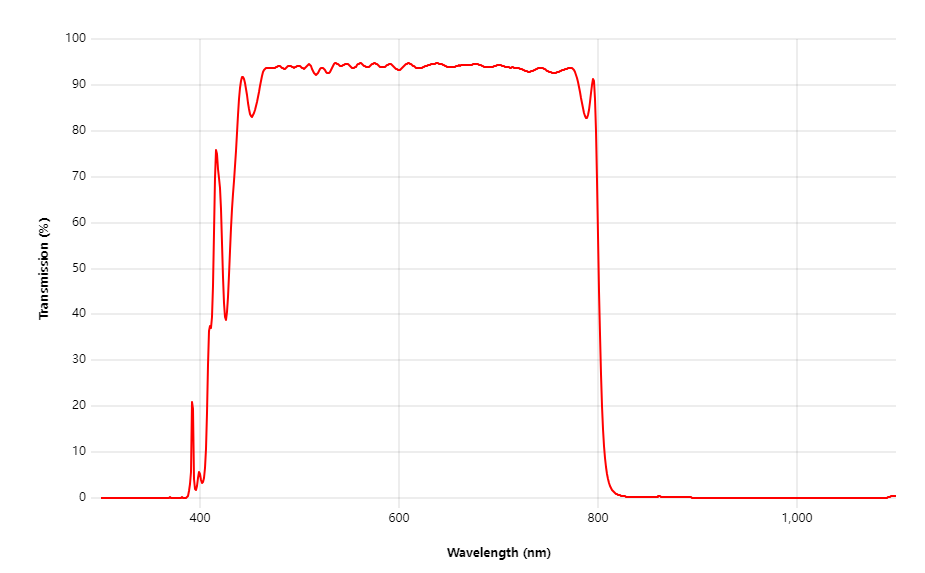
The wavelength range of IR cut filters determines their effectiveness. Typically, these filters block infrared light above 700 nm while allowing visible light to pass through. Some advanced filters, such as Optolong Optics’ UV IR Cut Filter 800nm, block ultraviolet and infrared light at the 800nm edge wavelength.
This feature ensures that only the visible spectrum reaches the camera sensor. Accurate wavelength blocking can better maintain color fidelity and image clarity.
Transmission Efficiency of IR Cut Filters
Transmission efficiency measures how well an IR cut filter allows visible light to pass through. High transmission can better capture clear and vivid images. For example, the 800nm UV IR Cut Filter has a high transmission of Tmin>85%.
This high efficiency ensures minimal light loss, thereby improving overall image quality. Additionally, the blocking capability of the filter (e.g. OD>2 in the 850-1100 nm band) prevents unwanted infrared light from distorting the image.
Applications of IR-cut filters

Digital cameras
IR-cut filters block infrared light that can cause color distortion in digital cameras. By allowing only visible light to reach the sensor, the filter ensures accurate color reproduction. This results in clearer, more vivid images. The filter also improves contrast and clarity. This allows machine vision algorithms to detect and analyze objects more accurately.
Digital cameras are often required to work in a variety of lighting conditions. IR-cut filters help achieve this versatility. During the day, the filter blocks infrared light to maintain color accuracy. At night, the filter can be removed or turned off. This allows infrared light to enhance night vision.
Security cameras
Security cameras rely heavily on IR-cut filters. These filters block infrared light during the day. This prevents color shifts and ensures accurate color images. At night, the filter allows infrared light to pass through. This enhances night vision. This allows the camera to capture clear images even in low-light conditions.
Glare and reflections can degrade image quality. IR-cut filters help alleviate these problems. By blocking infrared light, the filter reduces unwanted glare. This results in clearer, more detailed images. These features allow security cameras to more accurately identify objects and individuals.
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging systems also use IR-cut filters, which ensure accurate color reproduction and allow for better diagnosis of medical conditions. The filters block infrared light that can cause color distortion. This results in clearer, more accurate images. Medical professionals can make more informed decisions.
Industrial Inspection
Industrial inspection systems benefit from IR-cut filters. These filters improve image quality by blocking infrared light. This ensures accurate color reproduction and improves image clarity.
Filters help detect defects and irregularities in products. This can increase the level of quality control and improve product standards.
Smartphones
Modern smartphones often contain IR-cut filters. These filters improve photo quality by blocking infrared light. This ensures accurate color reproduction in smartphone cameras.
IR-cut filters also enhance low-light performance. Many high-end smartphones are equipped with advanced IR-cut filters. These filters help improve the overall imaging capabilities of the device. Users can use these filters to take clearer, more vivid photos.
Drones
Drones equipped with cameras benefit from IR-cut filters. These filters ensure an accurate representation of colors in aerial photography.
IR-cut filters block infrared light that can cause color distortion. This makes images captured by drone cameras clearer and more detailed. Many professional drones have IR-cut filters built in. These filters improve the quality of aerial photography.
Summary
Infrared cut filters are used in modern imaging technology to improve color accuracy and image quality in various applications. Future advancements may focus on improving transmission efficiency and integration with more devices.
The growing demand for high-quality imaging has driven innovation in infrared cut filter technology. Optolong Optics’ UV IR cut filters can achieve high-quality imaging performance and accurate color rendering. Please contact us for precise information and relevant quotes!
Related reading: What is a Dichroic Mirror
