UV bandpass filters selectively transmit ultraviolet (UV) light while blocking other wavelengths of light. These filters enable precise control of UV radiation in a variety of applications. UV bandpass filters come in many types, each with its own unique materials and construction methods.
Let’s read this article to explore the definition of UV bandpass filters and the unique advantages of its various types in order to choose the most suitable filter for a specific purpose.
What Is a UV Bandpass Filter
A UV bandpass filter is a filter that transmits UV rays and blocks other wavelengths. These optical filters are widely used in scientific, industrial and medical applications. The transmittance of UV bandpass filters is generally 15-30%. Due to material reasons, most UV bandpass filters cannot be highly transparent.
But the core function of a UV bandpass filter is the ability to isolate specific UV wavelengths, which is useful in a variety of applications, from forensic analysis to sterilization processes.
UV Bandpass Filter Wavelength Range
UV bandpass filters typically cover the UV spectrum from about 200 nm to 400 nm. Here are some common ranges in this UV spectrum:
- UV-A: 315 to 400 nm. This range is typically used in applications involving black light or forensic analysis.
- UV-B: 280 to 315 nm. Filters for this range are used in medical applications such as phototherapy.
- UV-C: 100 to 280 nm. It is widely used for sterilization and sterilization purposes, especially around 254 nanometers, which has a very strong sterilization effect.
What Is the Function of UV Bandpass Filter?
1. 1. Imaging and Photography Applications
UV band filters are widely used in imaging technology and are particularly suitable for capturing the reflection or emission properties of UV light. UV filters in general photography are mainly used to block ultraviolet light below 400nm while allowing visible light between 400-700nm to pass through.
In forensic science, the use of UV filters can reveal traces of blood, body fluids, and steganography that are invisible under normal lighting.
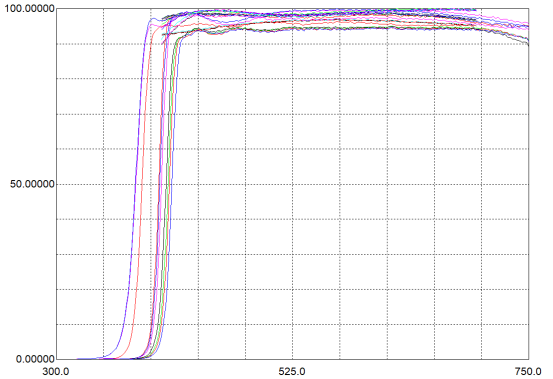
2. Scientific Research
In scientific research, UV filters are essential for observing substances that exhibit specific reactions under UV light. For example, in biological research, by using UV filters to observe the fluorescence response of biological samples, scientists can identify and track specific molecules and proteins within cells.
3. Industrial Applications
In industry, UV filters are widely used in quality control processes. For example, in semiconductor manufacturing, UV filters are used to detect tiny flaws and contaminants on chip surfaces. In addition, these filters are used to check for unevenness and defects in coatings and plastic products to ensure product quality.
4. Medical and Health
In the medical field, ultraviolet light is one of the most effective ways to kill viruses and bacteria. Meanwhile, in clinical diagnosis, UV filters help diagnostic equipment accurately observe the fluorescent response of microorganisms and other biomarkers in body fluid samples.
5. Astronomy
Astronomers use specific types of UV filters to study objects that primarily emit UV wavelengths, such as Optolong’s Venus-U filter, which can be used to observe Venus.
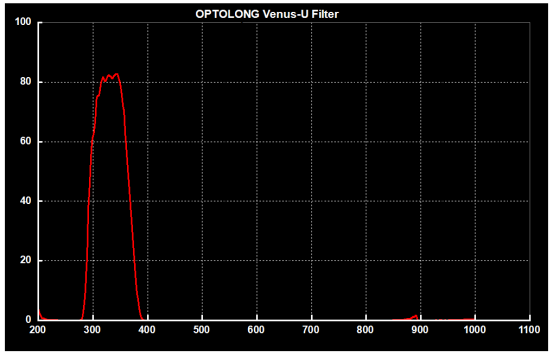
This type of bandpass filter not only helps observe celestial objects such as Venus, but also allows in-depth study of star formation and galaxy evolution in the universe by analyzing the ultraviolet radiation of these objects.
Types of UV Bandpass Filters
There are many types of UV bandpass filters, each designed to meet the specific requirements of different applications. Here is a detailed description of some common types of UV bandpass filters:
1. Narrowband UV Filter
Narrowband UV filters transmit primarily a very narrow range of UV wavelengths while blocking other visible and infrared light. These filters are highly selective and ideal for scientific and medical applications where precise wavelength isolation is critical, such as fluorescence microscopy or analytical instruments that measure specific UV-absorbing compounds.
2. Broadband UVFilter
Unlike narrowband filters, broadband UV filters allow a wider range of UV wavelengths to pass. These filters are used in applications that require a broader spectral response, such as solar UV research or environmental monitoring where multiple UV wavelengths are required to detect or measure various substances.
3. Dual-Band UV Filter
A dual-band UV filter is a specialized filter capable of transmitting two different wavelength ranges, typically one in the UV and one in the visible or infrared spectrum. These filters can be used in multispectral imaging systems that need to capture images in ultraviolet and other wavelength bands simultaneously.
4. Steep EdgeUV Bandpass Filter
These filters are characterized by their ability to provide a clear cutoff between the UV wavelengths transmitted and the visible light blocked. This steep transition is often applied in forensic analysis where all visible light must be eliminated to see only UV-induced fluorescence, or in systems where high optical performance and low light loss are required.
5. Customized UV Bandpass Filter
For specific applications, custom UV bandpass filters can be designed and manufactured to meet unique requirements. For example, Optolong Optics, their website not only provides a variety of optical filters, but also provides users with a variety of customized filters services to help users solve incompatibility issues.
Each type of UV bandpass filter serves a unique purpose and is optimized for different performance characteristics (such as bandwidth, transmission efficiency, and blocking capabilities) to effectively fit a variety of UV applications.
What Should You Consider When Choosing a Uv Bandpass Filter?
When choosing a UV bandpass filter, you can decide which type of filter to choose by considering the following points.
- Choose a filter whose center wavelength matches your application needs.
- Filters with high transmittance are preferred to provide brighter, clearer images.
- Make sure the filter effectively blocks non-UV light.
- Choose filters whose material is resistant to UV degradation and has a high surface quality.
- Just make sure the filter size is compatible with your device.
- Consider selecting filters that can withstand extreme conditions in the operating environment.
- Choose the best filter within your budget and consider supply chain factors.
Summarize
In summary, after understanding some basic information about UV bandpass filters, I believe you will have certain insights and judgments. Before making a choice for your application, you should be well prepared with a budget buying guide, which will help you make a decision faster.
If you don’t know how to choose and judge, you can contact our optolong professionals, who will give you detailed answers based on your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can UV Bandpass Filters Be Customized?
Yes, UV bandpass filters can be customized to meet the specific requirements of an application. This includes adjustments to diameter, thickness, substrate material and spectral properties.
2. What Materials Are Used in the Construction of UV Bandpass Filters?
UV bandpass filters are typically made from materials such as fused silica or borosilicate glass, which are chosen for their ability to withstand high-energy UV radiation and environmental durability.
Related reading: What is dichroic mirror
